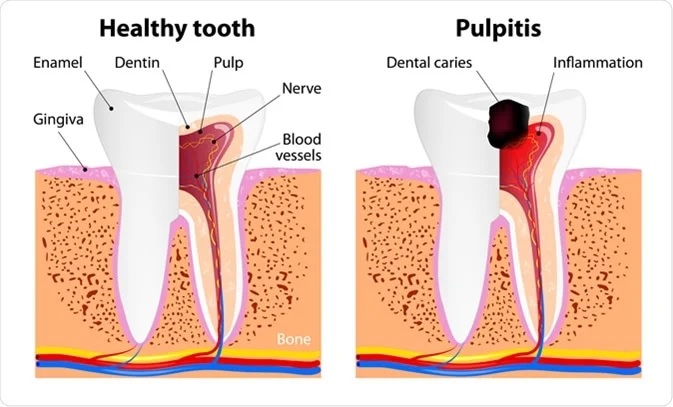
Milk Tooth Pulpitis is a pathological condition in which inflammation of the internal tissue of the tooth (pulp) occurs. The pulp is a collection of nerve fibers, connective tissue, blood and lymph vessels. It is responsible for the blood supply, nutrition, and innervation of the tooth, prevents the penetration of pathogenic elements into the root canals and periodontium, and promotes the formation of new tissues when a unit is damaged by a carious process.
Causes Of The Disease:-
The main and most common cause is caries, in which bacteria and their metabolic products strongly destroy hard dental tissues and penetrate into the pulp, causing an inflammatory process.
Other factors that can lead to pulpitis directly or indirectly are:
- tooth injuries, when the pulp chamber is exposed due to the breakage of the coronal part;
- acute and chronic infectious diseases that have a negative impact on the work of local and general immunity;
- incomplete or incorrectly performed treatment of caries, stomatitis, and gingivitis in children ;
- infection through the bloodstream and root canals;
- installation of low-quality filling material.
In some cases, the cause is too aggressive exposure to antiseptics and other means to treat the problem unit during dental treatment. Milk teeth have a more porous and loose structure, due to which the enamel absorbs substances that have fallen on it faster and may begin to break down.
Signs Of Acute Pulpitis:-
Acute forms of the disease in childhood are less common than chronic ones, due to the peculiarities of the structure of the milk dentition. The infection develops so rapidly that almost always the acute condition becomes chronic even before the start of therapeutic treatment.
Symptoms of acute pulpitis can be:
- sharp, throbbing pain in the tooth, aggravated at night and during sleep;
- severe swelling, redness of the gums and mucous tissues in the area of the affected unit;
- discomfort, severe pain when pressing on the tooth, getting cold liquids or food on it, while chewing hard ingredients;
- increased body temperature;
- general weakness, malaise.
In some cases, with extensive inflammation, purulent fluid is released from the gums or dental cavity, sometimes with blood impurities. In a number of children, the submandibular and cervical lymph nodes also swell, and a headache is observed.
Signs Of Chronic Pulpitis:-
Almost always, this form of pathology becomes the next stage of acute pulpitis, but in some cases, against the background of extensive carious processes, it can become a primary and independent disease.
The main symptoms of chronic pulpitis in children are:
- slight pain with pressure on the tooth, getting warm or hot liquid on it, while eating;
- periodic discharge of blood from the carious cavity, especially during brushing your teeth;
- The proliferation of pulp tissue inside the carious cavity in the form of a dense ball;
- unpleasant odor from the oral cavity even after careful hygiene procedures;
- general fatigue, rapid fatigue of the child.
If the process is extensive, there are volumetric destructions, the infected tooth becomes gray and very fragile. While eating, the child periodically spits out fragments of teeth, feels the taste of iron due to blood.
Treatment Of Chronic And Acute Pulpitis In Childhood-
To eliminate the problem, pediatric dentists use conservative and surgical techniques. In general, the treatment of dental pulpitis in children differs little from the treatment of a similar disease in adult patients: all the efforts of doctors are aimed at preserving the natural unit, stopping the inflammatory process and preventing complications.
Conservative options include:
- A biological technique, when a doctor puts drugs into the carious cavity for a certain time to suppress pathogenic elements, and then closes the tooth with a filling;
- Amputation, in which the damaged coronal part of the pulp is removed, and the root part is preserved.
- In cases where the damage is too extensive, conservative tactics do not bring the desired result, or there is a high risk of complications, doctors resort to radical surgical methods:
- Devital extirpation, when during the first visits special pastes and ointments are placed in the tooth cavity, which kill bacteria and the pulp itself, and then, with the help of surgical instruments, tissue remnants are removed, the canals are cleaned and sealed, the unit is closed with a filling;
- vital extirpation, when the pulp is removed immediately in one visit without additional procedures.
The choice of technique depends on the form and severity of the disease, the presence of allergic diseases in the child, and other individual parameters of the patient. For more tips about health beauty and fitness visit our site.
You May Also Like:- Inattention: How To Improve Concentration